元2022 12月 中国
脳卒中患者の移動能力評価にはおもに前進歩行速度がもちいられる。
機能回復が良好な患者についてはさらに難易度の高いテストをおこなうことで移動能力の障害をあきらかにできる。
後ろ歩きが移動性障害のスクリーニングに敏感であるとする報告があるが、判別のためのカットオフ速度はわかっていないので、くわしくしらべてみたそうな。
元2022 12月 中国
元2020 7月 中国
元
2020 5月 イタリア
元
Assessment of backward walking unmasks mobility impairments in post-stroke community ambulators
2019 5月 アメリカ
元
A Backward Walking Training Program to Improve Balance and Mobility in Acute Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.
2017 12月 アメリカ
・トレーニング直後、前方歩行速度は BWT: 0.75 m/s; SBT: 0.41 m/s、
・後方歩行速度は BWT: 0.53 m/s; SBT: 0.23 m/s で いずれもBWTグループが高く、
・1ヶ月後もBWTグループがすぐれていた。
・バランス能力も "Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale" でBWTグループがあきらかにすぐれていた。
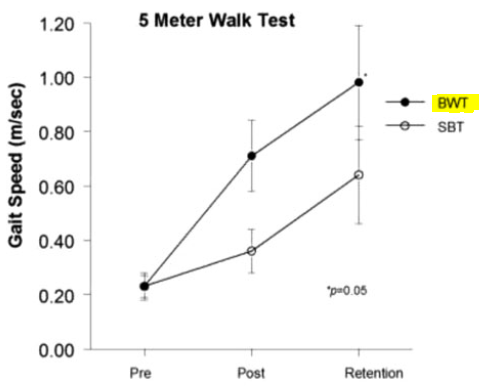
後ろ歩きの効果をきっちりと検証することにした
元
Comparison of the Effect of Lateral and Backward Walking Training on Walking Function in Patients with Poststroke Hemiplegia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.
2016 6月 韓国
・歩行速度、歩幅、歩行対称性などの点で横歩きグループが他の2グループよりも明らかに改善度が高かった。

後ろ歩きの効果をきっちりと検証することにした
元
Effect of backward walking treadmill training on walking capacity after stroke: a randomized clinical trial.
2014 4月 ブラジル
88人の脳卒中経験者について、前向き歩行と後ろ向き歩行のグループに分けて
1回30分間x週3日x6週間の訓練を行う。
そして3ヶ月後まで効果をフォローする。
Gait outcomes after additional backward walking training in patients with stroke: a randomized controlled trial.